Subsea production systems are vital to the modern oil and gas industry, enabling the safe and efficient extraction of hydrocarbons from offshore reservoirs located beneath the seabed. As offshore exploration extends into deeper and more challenging environments, these systems provide a reliable solution for maximizing resource recovery while minimizing surface infrastructure. With increasing complexity, simulation technologies have emerged as essential tools for designing, testing, and operating subsea production systems, ensuring both safety and performance optimization.
Overview of Subsea Production Systems
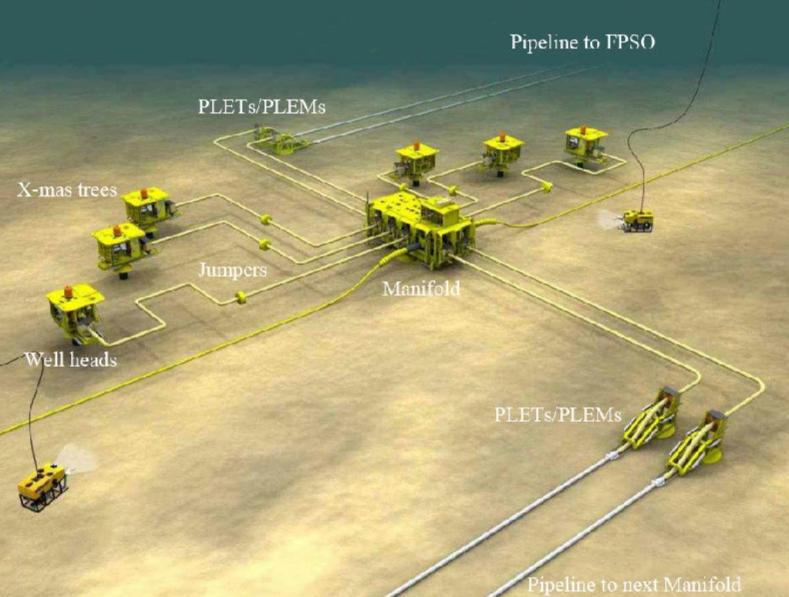
A subsea production system encompasses the infrastructure required to drill, extract, and transport oil and gas from underwater reservoirs to processing facilities. Typical components include subsea wells, manifolds, flowlines, risers, and control systems. Depending on field conditions, these systems may be tied back to a host platform, floating production storage and offloading unit (FPSO), or even connected directly to shore-based facilities.
Key advantages of subsea production systems include:
Ability to access reserves in ultra-deepwater environments.
Reduced need for large surface platforms, lowering capital expenditure.
Improved field development flexibility, especially in marginal fields.
Enhanced environmental performance through minimal surface footprint.
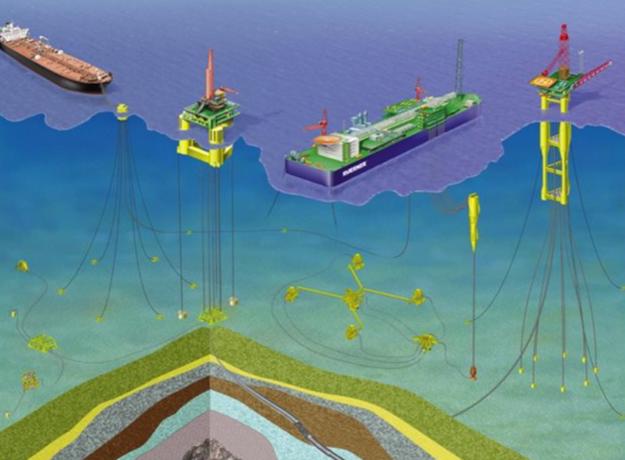

Challenges in Subsea Production
Operating in subsea environments presents several challenges:
Extreme pressures and low temperatures can lead to flow assurance problems such as hydrate and wax formation.
Maintenance and intervention are costly and logistically complex.
Integrity monitoring is critical to avoid leaks or equipment failures.
Increasing system complexity requires advanced engineering and operational expertise.
Role of Simulation Technologies
To address these challenges, simulation technologies play a pivotal role across the lifecycle of subsea production systems. They are applied in design, training, operational optimization, and risk management.
1. Design and Engineering
Oil and gas simulation tools allow engineers to model subsea layouts, fluid dynamics, and thermal behaviors under real-world conditions. Flow assurance simulations help predict hydrate formation, corrosion risks, and pressure drops, ensuring optimal equipment sizing and configuration before field deployment.
2. Operational Training
Operators and engineers can use immersive simulators to practice handling subsea control systems, emergency scenarios, and maintenance operations. This reduces human error and enhances response time in critical situations.
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Digital Twins
Digital twin technology, built upon simulation models, provides a virtual representation of subsea assets. Real-time data from sensors can be integrated into these models, enabling predictive maintenance, production optimization, and early detection of anomalies.
4. Risk and Safety Analysis
Dynamic simulations are used to analyze blowout scenarios, equipment failures, or flow interruptions. These predictive models help operators prepare contingency measures and design safer subsea systems.

Future Outlook
As the oil and gas industry pushes toward ultra-deepwater developments and more complex reservoir conditions, the integration of advanced simulation technologies will become even more critical. The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and high-fidelity simulation will enable autonomous monitoring and optimization of subsea systems. This not only enhances production efficiency but also ensures sustainability and environmental protection.
Summary
Subsea production systems are a cornerstone of offshore oil and gas development, enabling access to resources that were once out of reach. However, their complexity and operational risks necessitate the use of advanced simulation technologies. From design and training to real-time monitoring and risk analysis, simulations provide a powerful means of improving safety, reducing costs, and optimizing performance in subsea operations. As digitalization continues to evolve, simulation technologies will remain at the heart of innovation in subsea production systems.

























