In the fast-paced world of laboratory research, efficiency and precision are paramount. Two of the most commonly used pieces of equipment in labs are vortex mixers and centrifuges. While both serve critical functions, they are designed for distinct purposes and offer unique advantages. Understanding the differences between vortex mixers and centrifuges, as well as their respective roles in lab workflows, is essential for optimizing laboratory efficiency. This article explores the functionalities, applications, and comparative benefits of vortex mixers and centrifuges, helping researchers make informed decisions about their use.
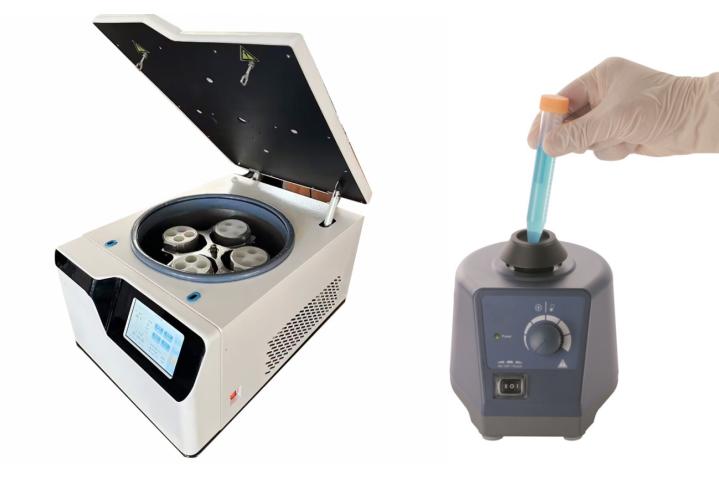

Vortex Mixers: Mixing with Precision
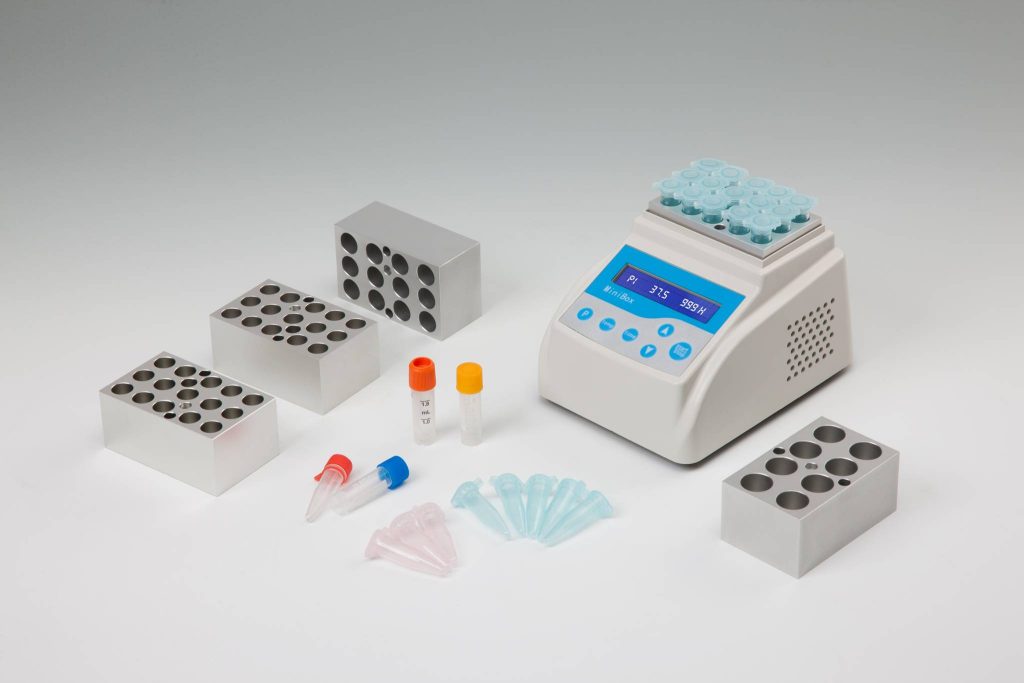
Vortex mixers are compact, versatile devices used to mix small volumes of liquids rapidly. They operate by creating a vortex—a circular motion that thoroughly mixes the contents of a tube or container. Vortex mixers are particularly valued for their simplicity, speed, and ability to handle multiple samples simultaneously.

Key Features and Applications of Vortex Mixers
Rapid Mixing: Vortex mixers excel at quickly homogenizing liquids, making them ideal for tasks such as resuspending pellets, mixing reagents, or blending samples.
Ease of Use: With straightforward operation and minimal setup, vortex mixers are user-friendly and require little training.
Compact Design: Their small footprint makes them suitable for labs with limited bench space.
Versatility: Vortex mixers can accommodate a variety of tube sizes and are often used in molecular biology, chemistry, and clinical labs.
Centrifuges: Separating with Power
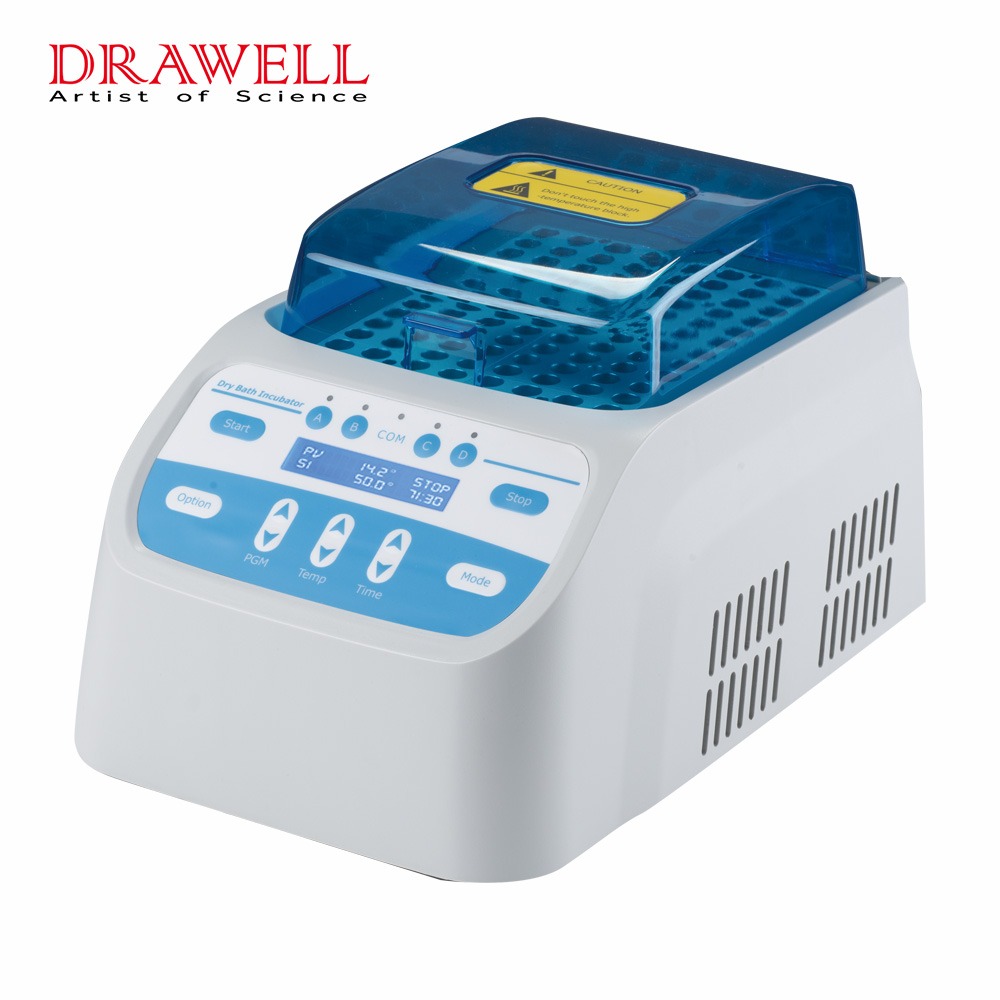
Centrifuges are powerful instruments designed to separate components of a mixture based on density. By spinning samples at high speeds, centrifuges generate centrifugal force, causing denser particles to settle at the bottom of the tube while lighter components remain suspended or form layers. Centrifuges are indispensable for tasks such as cell isolation, protein purification, and DNA extraction.

Key Features and Applications of Centrifuges
Separation Efficiency: Centrifuges are unmatched in their ability to separate complex mixtures, making them essential for applications like blood sample processing, cell culture, and molecular biology.
High-Speed Operation: Modern centrifuges can reach extremely high speeds, enabling rapid and precise separation of samples.
Scalability: Centrifuges come in various sizes and configurations, from microcentrifuges for small volumes to large floor models for high-throughput applications.
Specialized Functions: Many centrifuges offer advanced features, such as temperature control and programmable settings, to accommodate specific experimental needs.
Comparing Vortex Mixers and Centrifuges
While both vortex mixers and centrifuges are essential lab tools, they serve different purposes and are often used in complementary ways. Here’s a comparison of their roles in lab efficiency:
Functionality:
Vortex mixers are designed for mixing and homogenizing liquids, ensuring even distribution of components.
Centrifuges are designed for separating components based on density, enabling the isolation of specific materials.
Speed and Throughput:
Vortex mixers provide near-instantaneous mixing, making them ideal for quick tasks.
Centrifuges require longer run times but offer unparalleled separation capabilities.
Sample Volume:
Vortex mixers are best suited for small volumes, typically in tubes or microplates.
Centrifuges can handle a wide range of volumes, from microliters to liters, depending on the model.
Applications:
Vortex mixers are commonly used for preparing samples, mixing reagents, and resuspending pellets.
Centrifuges are essential for isolating cells, purifying proteins, and separating phases in complex mixtures.
Space and Cost:
Vortex mixers are compact and generally more affordable, making them accessible for most labs.
Centrifuges, especially high-speed or refrigerated models, are larger and more expensive, requiring a greater investment.
Optimizing Lab Efficiency with Vortex Mixers and Centrifuges
To maximize lab efficiency, researchers should consider the specific requirements of their experiments and workflows. Vortex mixers are invaluable for tasks that demand quick and thorough mixing, while centrifuges are indispensable for separation and purification processes. In many cases, these tools are used in tandem—for example, vortexing a sample to mix reagents before centrifuging it to isolate the desired components.
In conclusion, vortex mixers and centrifuges are both critical to laboratory efficiency, but they serve distinct roles in the research process. Vortex mixers excel at rapid mixing and homogenization, while centrifuges are unmatched in their ability to separate complex mixtures. By understanding the strengths and applications of each tool, researchers can optimize their workflows, improve experimental outcomes, and enhance overall lab productivity. Whether used independently or together, vortex mixers and centrifuges remain foundational instruments in the pursuit of scientific discovery.