Reservoir simulation is a crucial computational tool used in petroleum engineering to model the behavior of fluids (oil, gas, and water) within a reservoir over time. By integrating geological, geophysical, petrophysical, and production data, reservoir simulation provides a dynamic representation of subsurface reservoirs. This process enables engineers and geoscientists to predict reservoir performance, optimize production strategies, and make informed decisions on field development.
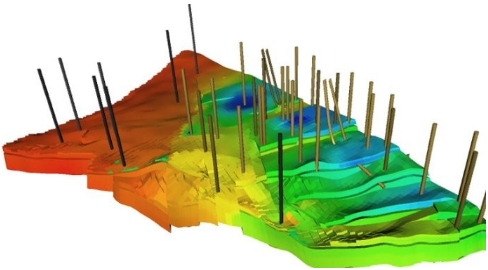
Understanding Reservoir Simulation
At its core, reservoir simulation is the mathematical modeling of multiphase fluid flow within porous media. This is achieved by solving a set of nonlinear partial differential equations that govern mass conservation, momentum, and energy transfer. These oil and gas simulations often require vast computational resources and sophisticated software platforms capable of handling complex reservoir geometries and fluid properties.
The model typically includes:
Reservoir Geometry and Grid System: The reservoir is divided into a 3D grid of cells, each characterized by parameters such as porosity, permeability, pressure, and fluid saturation.
Rock and Fluid Properties: Accurate representations of how rock and fluids behave under changing pressure and temperature conditions are essential.
Initial and Boundary Conditions: Historical data and expected external interactions (e.g., injection wells, aquifer support) are factored in.
Production History and Forecasting: Simulation uses past production data to calibrate the model and forecast future performance under various scenarios.
Key Applications of Reservoir Simulation
Field Development Planning: By simulating different well placements and production strategies, engineers can identify optimal drilling locations and production schemes.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): Simulations help evaluate the impact of EOR techniques such as water flooding, gas injection, or chemical EOR on recovery efficiency.
Reservoir Management: Real-time reservoir simulation supports decision-making in day-to-day operations, including well control and reservoir pressure management.
Economic Evaluation: Simulation results feed into economic models that assess the profitability and risks of development projects.
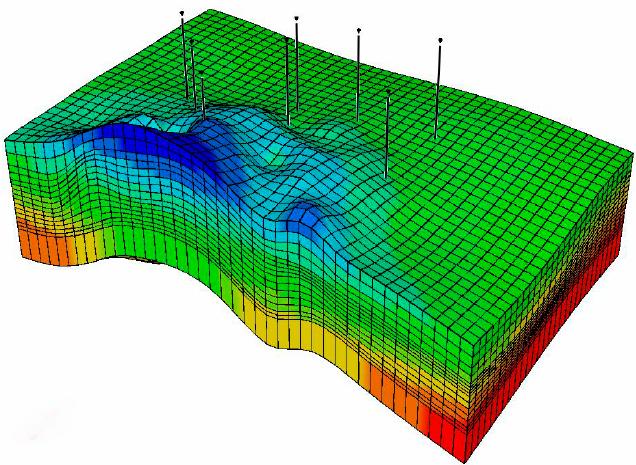
Types of Reservoir Simulation Models
Black-Oil Models: Simplified models that assume three fluid phases—oil, water, and gas—are immiscible and are used when compositional changes are not significant.
Compositional Models: More complex models accounting for the composition of hydrocarbons, suitable for volatile oil and gas condensate reservoirs.
Thermal Models: Used for reservoirs where heat plays a significant role in recovery processes (e.g., steam injection in heavy oil recovery).
Dual-Porosity Models: Designed to simulate fractured reservoirs where the matrix and fractures have separate flow characteristics.
Benefits of Reservoir Simulation
Improved Recovery Efficiency: Oil recovery simulation identifies zones with bypassed oil and optimizes recovery techniques.

Risk Mitigation: By modeling various scenarios, operators can anticipate and mitigate geological or operational risks.
Cost Savings: Simulation reduces the need for trial-and-error field experimentation, leading to more efficient resource allocation.
Support for Digital Oilfields: Integrates with real-time monitoring systems to support dynamic reservoir management.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its benefits, reservoir simulation faces challenges such as:
Data Uncertainty: Incomplete or low-resolution subsurface data can affect model accuracy.
Computational Demands: High-resolution models require substantial computational power and time.
Integration Complexity: Coordinating input data from different domains (geology, geophysics, production) remains a technical hurdle.
Future advancements are expected in the areas of:
Machine Learning Integration: AI can speed up history matching and improve prediction accuracy.
High-Performance Computing (HPC): Will enable real-time simulation with finer grids and more detailed physics.
Cloud-Based Platforms: Facilitate collaboration and accessibility across teams and geographies.
Final Thoughts
Reservoir simulation is a foundational element of modern reservoir engineering. By providing a comprehensive view of subsurface behavior, it enables more accurate forecasting, strategic planning, and optimal resource extraction. As digital technologies continue to evolve, reservoir simulation will become increasingly integral to the efficient and sustainable development of hydrocarbon resources.