The oil and gas industry utilizes various drilling techniques, each suited for specific conditions, resource locations, and operational objectives. A comparative analysis of drilling methods highlights the advantages, limitations, and ideal applications of each. Understanding these methods can help stakeholders select the most appropriate approach based on factors such as efficiency, cost, safety, and environmental considerations.

1. Conventional Vertical Drilling
Overview:
Conventional vertical drilling is the traditional approach, where the well is drilled straight down from the surface to reach an oil or gas reservoir. This method is straightforward, cost-effective, and widely used in regions where reservoirs are directly below the drilling site.
Advantages:
Lower Cost: Vertical drilling is often less expensive due to its simplicity, lower equipment requirements, and reduced complexity.
Simplicity and Speed: Fewer moving parts and shorter drill paths allow for faster drilling and completion.
Ease of Maintenance: Equipment and well maintenance are generally less complex, making it a preferred option in remote areas.
Limitations:
Limited Reservoir Access: Vertical wells are effective only in reservoirs that lie directly beneath the drill site, making them unsuitable for larger or unconventional reservoirs.
Lower Recovery Rates: Compared to advanced methods, vertical wells typically access less of the reservoir, resulting in potentially lower yields.
Environmental Impact: Multiple vertical wells are often required to cover an area, increasing land disturbance.
Ideal Applications:
Shallow or directly accessible reservoirs, smaller oil fields, and wells with low environmental restrictions are ideal for vertical drilling.
2. Directional Drilling
Overview:
Directional drilling enables operators to drill at various angles, allowing for multiple well paths to diverge from a single drill site. This approach is widely adopted for accessing resources spread across a broader area or where geological formations make vertical access impractical.
Advantages:
Increased Reservoir Contact: By adjusting the angle, operators can target multiple points within a reservoir, significantly increasing recovery rates.
Environmental Benefits: A single well pad can support multiple deviated wells, minimizing the environmental footprint.
Cost-Effective Multi-Well Pads: Drilling multiple wells from one location reduces costs associated with site preparation and surface equipment.
Limitations:
Higher Initial Costs: The equipment and technology for directional drilling are more costly than conventional vertical drilling.
Complex Operations: The additional engineering and planning required increase operational complexity and demand skilled personnel.
Ideal Applications:
Directional drilling is ideal for offshore and onshore reservoirs where the resource extends horizontally or where regulatory and environmental considerations limit the number of well pads.
3. Horizontal Drilling
Overview:
Horizontal drilling is an extension of directional drilling where the well is first drilled vertically and then gradually turned horizontally to maximize contact with the oil or gas reservoir. Horizontal wells are critical in the development of unconventional resources, such as shale and tight gas formations.
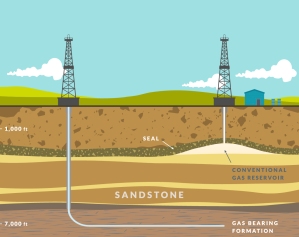
Advantages:
Enhanced Resource Recovery: Horizontal wells maximize reservoir exposure, significantly increasing production, especially in low-permeability reservoirs.
Efficient Resource Drainage: Horizontal wells can effectively drain large areas of a reservoir, reducing the need for multiple wells.
Compatibility with Hydraulic Fracturing: Horizontal drilling works well in conjunction with hydraulic fracturing to release resources in tight formations.
Limitations:
Higher Drilling Costs: Horizontal drilling requires advanced equipment and specialized techniques, increasing initial expenses.
Complex Well Design: Complex engineering and planning are required, as well as experienced drillers, which may limit its applicability in certain regions.
Ideal Applications:
Horizontal drilling is particularly suited to unconventional plays, including shale gas, shale oil, and coalbed methane, where maximizing contact with the resource layer is essential for economic viability.
4. Rotary Steerable Drilling (RSS)
Overview:
Rotary steerable drilling systems allow for precise steering of the drill bit without interrupting the drilling process. Unlike traditional steerable systems, RSS maintains continuous rotation of the drill string, improving drilling efficiency and allowing for highly accurate well placement.
Advantages:
Enhanced Accuracy and Control: RSS provides real-time directional adjustments, which are essential for complex or extended-reach wells.
Improved Drilling Speed: Continuous rotation prevents the need to stop and adjust, leading to faster drilling and lower costs.
Ideal for Extended-Reach Drilling (ERD): RSS technology makes it feasible to drill longer wells with fewer deviations, maximizing reservoir exposure.
Limitations:
High Equipment and Operational Costs: RSS systems are among the most expensive due to the technology and real-time monitoring required.
Requirement for Skilled Operators: Operating RSS requires specialized skills and training, which can limit its application where such personnel are unavailable.
Ideal Applications:
RSS is ideal for deepwater offshore drilling, extended-reach drilling, and wells with complex geological formations, where precision and control are crucial.
Technological Advancements in Drilling Methods
The drilling industry is experiencing transformative changes with advancements in technology, making drilling safer, more efficient, and capable of reaching previously inaccessible resources. Here’s a look at some of the front-line innovations:
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are replacing labor-intensive tasks in drilling, enhancing both safety and efficiency. Robotic arms can perform precise tasks at the borehole without fatigue, reducing human error and allowing for continuous operation. Think of it as having a tireless assistant performing delicate maneuvers in high-risk environments, ensuring reliability and reducing downtime.
Data Analytics and Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time data analytics and monitoring systems are revolutionizing the decision-making process. Sensors and advanced software continuously track the health and stability of the wellbore, acting as a vigilant, subterranean doctor that instantly identifies issues and recommends adjustments. This data-driven approach minimizes costly mistakes, increases efficiency, and helps operators maintain optimal drilling conditions at all times.
Advanced Drilling Fluids
Nano-engineered drilling fluids are redefining wellbore stability, cooling, and lubrication capabilities. These high-performance fluids are designed to perform under extreme conditions, enabling access to deeper and more challenging formations. Imagine these fluids as a “magic potion” that boosts drilling efficiency, stability, and safety in some of the harshest environments.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI algorithms are making drilling operations smarter by predicting potential issues, recommending ideal techniques, and autonomously adjusting drilling parameters for optimal performance. Picture a drilling mastermind that anticipates and solves problems before they arise, ensuring safer and more efficient operations by continuously learning from past data to improve future outcomes.
Drilling Simulation
Drilling simulation technology offers a risk-free platform to train personnel and analyze various scenarios. These simulations provide realistic, immersive environments for drillers to practice and refine their skills, allowing them to tackle complex scenarios with confidence.

To sum up, each drilling method in the oil and gas industry has distinct advantages and limitations, making it essential to choose the most appropriate one based on the specific characteristics of the reservoir, operational goals, and budgetary constraints. Vertical drilling remains a practical choice for shallow and easily accessible reservoirs, while directional and horizontal drilling expand the range of accessible resources and improve yield in larger fields. Rotary steerable drilling offers unmatched control and efficiency, especially for complex or deepwater projects. By selecting the best-suited drilling technique, operators can maximize productivity, reduce costs, and achieve higher environmental stewardship.
























