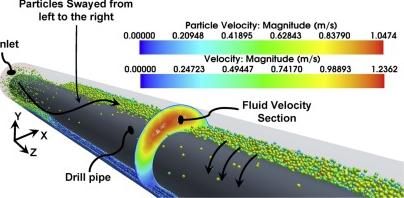
The oil and gas industry has long been a cornerstone of global energy production, but it is also a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO₂). As the world transitions toward a low-carbon future, Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) has emerged as a critical technology to reduce emissions while maintaining energy security. CCS is especially relevant in oil and gas drilling, where it can mitigate the environmental impact of fossil fuel extraction and processing. This article explores how CCS is applied in the oil and gas industry, its benefits, challenges, and its role in shaping a more sustainable energy future.
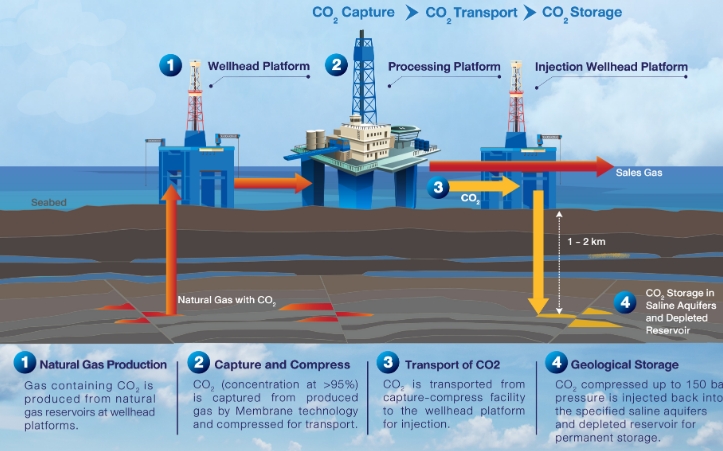
What is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)?
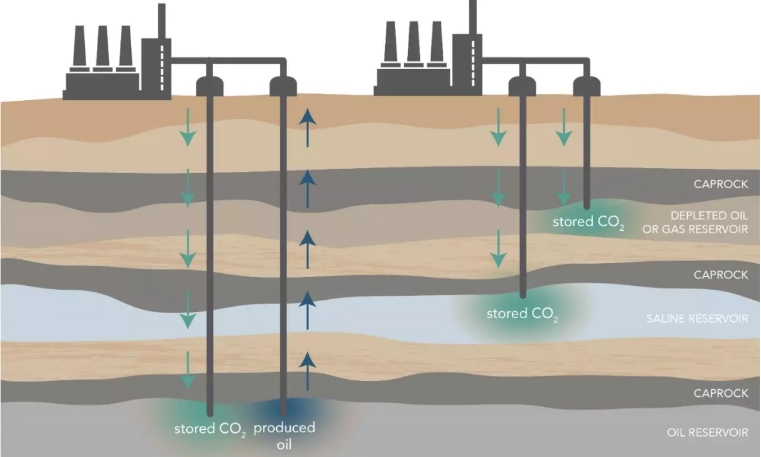
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a process that captures CO₂ emissions from industrial sources, transports them to a storage site, and securely stores them underground to prevent their release into the atmosphere. The process involves three main steps:
Capture: CO₂ is separated from other gases produced during industrial processes, such as power generation or oil and gas drilling.
Transport: The captured CO₂ is compressed and transported via pipelines, ships, or trucks to a storage site.
Storage: The CO₂ is injected deep underground into geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers, where it is permanently stored.
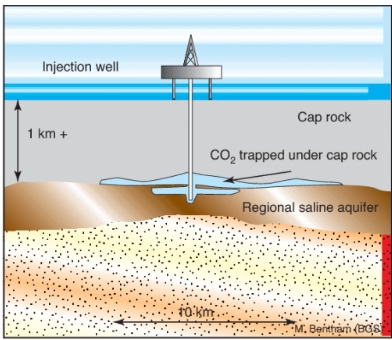
How CCS is Applied in Oil and Gas Drilling
The oil and gas industry is uniquely positioned to leverage CCS technology due to its expertise in subsurface operations and existing infrastructure. Here’s how CCS is applied in this sector:
1. Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR)
One of the most common applications of CCS in the oil and gas industry is Enhanced Oil Recovery(EOR). In this process, captured CO₂ is injected into depleted oil reservoirs to increase pressure and improve oil extraction. The CO₂ mixes with the oil, making it less viscous and easier to pump to the surface. This not only boosts oil production but also stores CO₂ underground, reducing emissions.
Example: The Petra Nova project in Texas, USA, captures CO₂ from a coal-fired power plant and uses it for EOR in an oil field.
2. Capturing Emissions from Upstream Operations
Oil and gas drilling operations release CO₂ during processes like flaring, venting, and fuel combustion. CCS can capture these emissions directly at the source, preventing them from entering the atmosphere.
Example: The Sleipner project in Norway captures CO₂ from natural gas production and stores it in a saline aquifer beneath the North Sea.
3. Decarbonizing Natural Gas Processing
Natural gas processing often involves separating CO₂ from raw natural gas to meet pipeline specifications. Instead of releasing the separated CO₂, CCS can capture and store it.
Example: The Gorgon CCS project in Australia captures CO₂ from natural gas production and injects it into a deep saline formation.
4. Reducing Emissions from Refineries
Oil refineries are significant sources of CO₂ emissions due to energy-intensive processes like cracking and reforming. CCS can be integrated into refineries to capture and store these emissions.
Example: The Quest CCS project in Canada captures CO₂ from a hydrogen production unit at an oil sands refinery and stores it underground.
Benefits of CCS in Oil and Gas Drilling
1. Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
CCS significantly reduces CO₂ emissions from oil and gas operations, helping the industry meet climate targets and regulatory requirements.
2. Enhanced Energy Security
By enabling the continued use of fossil fuels with lower emissions, CCS supports energy security during the transition to renewable energy sources.
3. Economic Opportunities
CCS creates new revenue streams, such as selling captured CO₂ for EOR, and supports job creation in engineering, construction, and operations.
4. Extended Life of Oil and Gas Assets
CCS allows oil and gas companies to extend the life of existing assets while reducing their environmental impact, providing a bridge to a low-carbon future.
5. Improved Public Perception
Adopting CCS demonstrates a commitment to sustainability, enhancing the industry’s reputation and social license to operate.
Challenges of Implementing CCS in Oil and Gas Drilling
1. High Costs
CCS is capital-intensive, requiring significant investment in capture technology, transportation infrastructure, and storage facilities.
2. Regulatory and Policy Barriers
Inconsistent regulations and lack of financial incentives (e.g., carbon pricing) can hinder CCS deployment.
3. Technical Risks
Ensuring the long-term stability and safety of CO₂ storage requires advanced monitoring and risk management.
4. Public Acceptance
Concerns about the safety and environmental impact of CO₂ storage can lead to opposition from local communities.
5. Infrastructure Limitations
Developing pipelines and storage sites requires significant time and resources, particularly in remote or offshore locations.
The Future of CCS in Oil and Gas Drilling
As the world strives to achieve net-zero emissions, CCS is expected to play a pivotal role in decarbonizing the oil and gas industry. Key trends and developments include:
1. Technological Advancements
Innovations in capture technology, such as solvent-based systems and membrane separation, are reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Simulation technologies used in oil and gas drilling, can model complex subsurface environments to predict CO₂ behavior, assess reservoir capacity, and evaluate potential leakage risks. By simulating injection processes and monitoring long-term storage performance, these technologies enhance the safety and efficiency of CCS operations. Key methods include reservoir simulation, geomechanical modeling, and fluid flow analysis, enabling accurate forecasting and improved decision-making throughout the CCS lifecycle.
2. Policy Support
Governments are increasingly recognizing the importance of CCS and introducing policies like tax credits, grants, and carbon pricing to incentivize adoption.
3. Collaborative Projects
Public-private partnerships and international collaborations are driving large-scale CCS projects, such as the Northern Lights initiative in Europe.
4. Integration with Renewable Energy
CCS can complement renewable energy by providing a reliable backup during periods of low wind or solar generation.
5. Carbon Utilization
Beyond storage, captured CO₂ can be used to produce synthetic fuels, chemicals, and building materials, creating new economic opportunities.
Conclusion
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a game-changing technology for the oil and gas industry, offering a practical solution to reduce emissions while maintaining energy production. By integrating CCS into drilling operations, the industry can significantly lower its carbon footprint, enhance energy security, and contribute to global climate goals. Although challenges remain, advancements in technology, policy support, and collaborative efforts are paving the way for widespread CCS adoption.