Mastering the operational skills of the patient monitor, also known as a heart monitor, is an essential competence for every medical nurse. When it comes to utilizing ECG monitors, there are crucial operational aspects that cannot be overlooked.
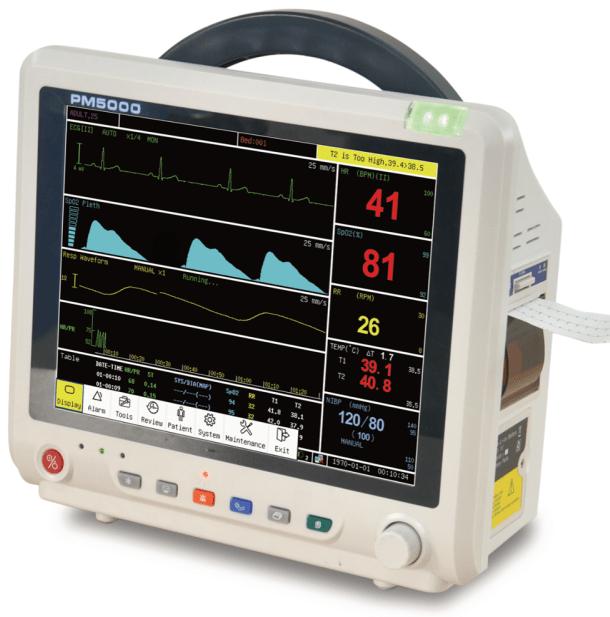
Key Considerations for Operating Patient Monitors
1. Distinction Between 3-Lead and 5-Lead ECG Leads
Distinctions between 3-lead and 5-lead ECG leads are pivotal. The 3-lead ECG lead configuration captures ECGs from leads I, II, and III, while the 5-lead ECG lead setup captures ECGs from leads I, II, III, AVR, AFV, AVL, and V.
To streamline the connection process, an efficient color marking system is employed for quick and accurate placement of electrode pads. The color sequence for 3-lead ECG leads is red, yellow, green or white, black, and red; for 5-lead ECG leads, it’s white, black, red, green, and brown.
It’s important to note that electrodes of the same color have distinct placements in the two lead configurations. Utilizing English abbreviations such as RA, LA, RL, LL, and C is more dependable for electrode positioning compared to relying solely on color memorization.
2. Prioritizing Blood Oxygen Saturation Finger Cuffs
The preference for blood oxygen saturation finger cuffs stems from their speedier application compared to connecting ECG lead wires. These cuffs enable rapid monitoring of pulse rate and blood oxygen saturation, allowing medical staff to swiftly evaluate fundamental patient vital signs.
3. Limb Placement of Cuffs
Placing both blood oxygen saturation finger cuffs and automatic blood pressure monitor cuffs on the same limb is not recommended due to potential blood flow obstruction during blood pressure measurement. This interference can lead to inaccurate blood oxygen saturation readings.
4. Electrode Replacement for Continuous ECG Monitoring
In cases of continuous ECG monitoring, regular replacement of electrode pads is necessary. Prolonged adherence of electrode pads to the same area can lead to skin rashes and blisters. Frequent skin condition assessments are crucial to prevent skin breakdown.
5. Non-Invasive Blood Pressure Monitoring Considerations
a. Avoid measuring blood pressure on limbs with internal fistula, hemiplegic limbs, limbs affected by breast cancer resection, infusion sites, edema, and hematoma skin damage.
b. Routinely change the measurement site to prevent complications like purpura, ischemia, and nerve damage from cuff friction.
c. Pay attention to cuff and pressure value selection and adjustment for different age groups, avoiding pressure levels suitable for adults in pediatric cases and vice versa.
6. Respiration Monitoring
The monitor’s respiration tracking relies on the thorax’s impedance changes sensed by the ECG electrode pads. Optimal placement of the sensing electrodes (lower left and upper right) is crucial for accurate respiration waveforms, particularly for patients who predominantly breathe abdominally.
7. Alarm Range Settings
Alarm range settings should prioritize patient safety, minimize noise disruption, and avoid turning off alarms except when absolutely necessary during rescue operations. Alarm parameters should encompass heart rate variations within 30% above and below the patient’s own heart rate, appropriate blood pressure thresholds, and oxygen saturation based on the patient’s condition.
8. Troubleshooting Waveform Display Issues
If the monitor fails to display waveforms, the following steps are recommended:
a. Verify proper electrode pad placement and quality, along with correct lead wire connections.
b. Confirm accurate lead mode connections according to the ECG monitor’s specifications.
c. If issues persist, check the contact quality of the “ECG signal line” on the parameter socket board, as well as potential faults in the ECG board, connecting lines, or main control board.
Patient Monitor Tips
Precise electrode pad application involves cleaning and preparing the skin, attaching ECG lead wires securely, and using appropriate cleaning solutions for optimal contact.
Patient and family education is vital to prevent unnecessary interference with the monitor and to ease any anxieties associated with its usage.
Regular maintenance includes electrode replacement, skin cleaning, and seeking professional assistance for substantial monitor abnormalities.
Proper grounding is crucial; ensure proper connection of the ground wire to the host’s rear panel and a reliable common ground terminal.
By adhering to these operational guidelines, medical professionals can proficiently operate patient monitors, ensuring accurate vital sign monitoring and patient safety.